
Community Definition and Identity
The state of Louisiana is in the deep south region of the United States. It is the 19th smallest state by area and the 25th most populated of the fifty states. Originally colonized by the French during the 18th century, it became U.S. territory as part of the Louisiana Purchase in 1803 and was admitted to the union in 1812. In Louisiana, local government units known elsewhere as counties are called parishes. The Louisiana capitol is Baton Rouge. The largest city is New Orleans, home to the historic port city New Orleans and famous for its unique cuisine, jazz and annual Mardi Gras. Other large cities in the state include Shreveport, Lafayette, Lake Charles, Monroe, Alexandria, Bossier City, Houma and Kenner, each with its unique sites and historical significance. Rural communities make up about 80% of the state with nearly 26% of our population living in these rural areas. The remaining 20% is urban and suburban.
Louisiana is one of the deep south states and surrounded by Mississippi, Arkansas and Georgia, all states of similar size and populations. In addition to the similar physical characteristics, these Louisiana neighbors also share similar health challenges. Louisiana is also one of the states with highest numbers of people suffering from effects of hypertension and Type II Diabetes due to obesity and factors involved with their quality of life. Untreated, undiagnosed or uncontrolled, these diseases can progress to organ failure. As of August 2, 2022, there were 1, 912 people in Louisiana waiting for an organ transplant: 482 people needing a transplant because of complications from Type II diabetes and 468 people needing a transplant because of complications of Hypertension - each disease preventable/ manageable with good health practices.
The parishes in green will be the initial target areas of focus and contain 1⁄3 of the state’s population. By targeting these parishes initially, we hope to have the greatest impact for improving public health and ultimately reducing the growing number of needed transplants in the state. These parishes also align with the current efforts underway in the Description of Existing Community Collaboration Efforts below.
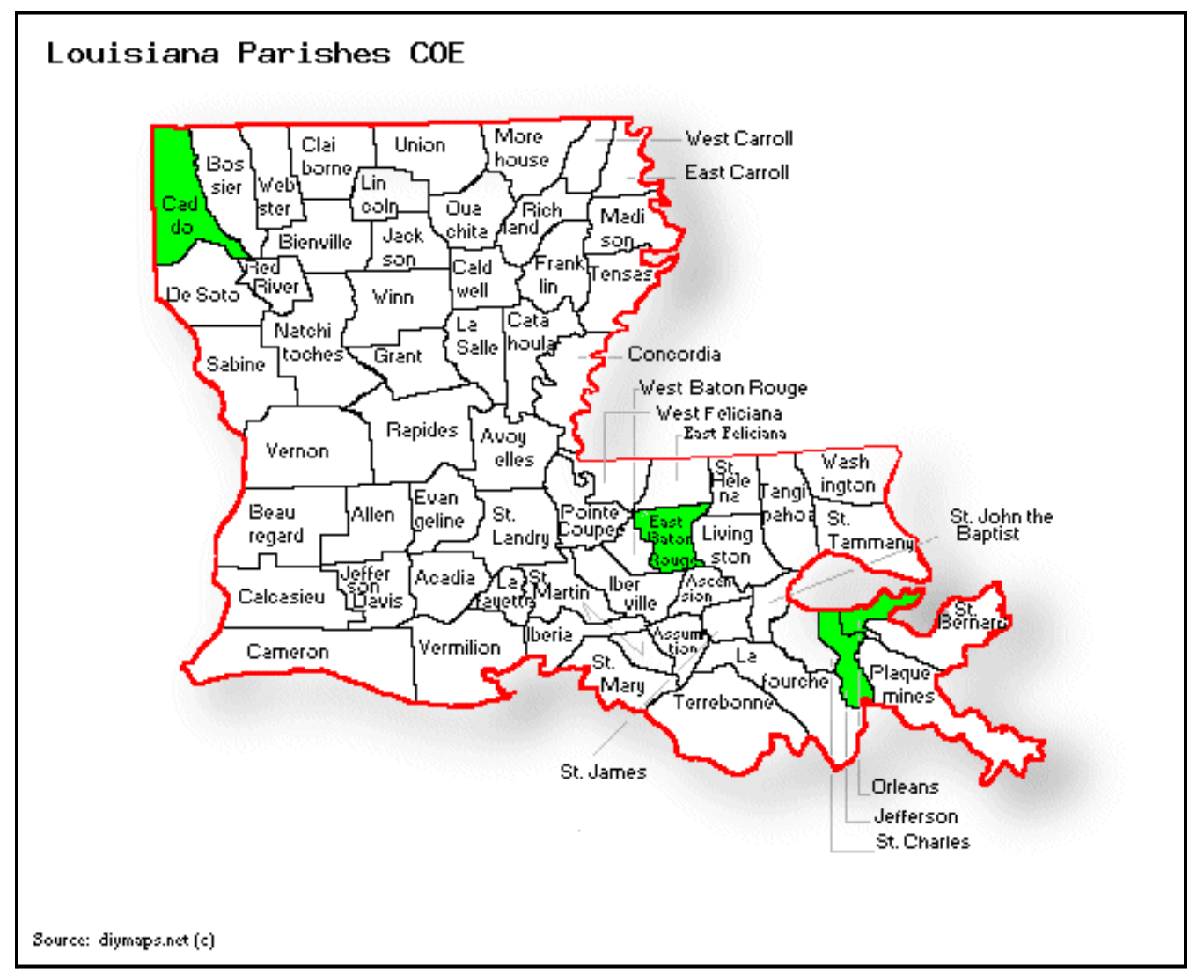
The total population of Louisiana is 4,627,002. This COE project is focused primarily on individuals living within the highest populated regions of Louisiana. For preliminary planning, we have selected the parishes of Orleans, Jefferson, East Baton Rouge and Caddo with populations of 1,502,900, or one third of the state's population. Orleans, Jefferson, East Baton Rouge and Caddo are all considered metropolitan areas. The ages and ethnicities in these selected parishes align well with the population on the organ transplant list in Louisiana: majority age over 35 years with the highest ethnicity being black and secondary ethnicity being white.
The community of the state of Louisiana is one that is resilient, relaxed and happy. As the state enjoys the best of many things, it also has some of the worst public health, an unending need for affordable housing and overall low incomes for many individuals and families and food insecurity.
The people of Louisiana are so familiar with addressing adversity that resilience is built into the cultural psyche of its citizens. When times are tough, neighbors will band together to rescue people from flooded areas, comfort and support those who have lost everything and help clean up disastrous messes. After any disaster, people will get out and help deliver gas, food, water and money to anyone in need. It's a cycle that repeats itself with each disaster: hurricanes Katrina and Rita in 2005, the BP Deepwater Horizon oil spill in 2010, the catastrophic 2016 floods, Hurricanes Laura and Delta in 2020 and Hurricane Ida in 2021.
Louisiana has become known as the place to come to eat, relax and “let the good times roll”. This laissez faire attitude makes the state a great vacation destination, but has also led to some of the poorest health in the country. The state ranks 46th in death due to heart disease and stroke, 47th in percentage of obese adults and 47th in percentage of adults with diabetes - all major precursors to organ failure, each preventable with good health habits (https://ldh.la.gov/index.cfm/newsroom/detail/2202).
Each year over 2000 men, women and children are listed to wait for a lifesaving organ in Louisiana. Many of these people were listed because of uncontrolled or unaddressed health issues. About 58% of the people listed are minorities. (Donate Life America https://www.donatelife.net/). The Social Determinants of Health (SDOH) are the conditions that residents live that result in a population's health. These conditions are driven by money power and resources and are unique at each location. In Louisiana, the SDOH that impacts community health the most have recently been identified as: housing, poverty levels and food insecurity. Communities in the state with inadequate housing, low household incomes and lack of access to healthy food are more at risk of suffering from poor health.
(https://www.livestories.com/statistics/louisiana/social-determinants-of-health).
In 2022, the median household income for the state was $50, 935. Louisiana is one of the poorest states in the U.S, with only Mississippi having more poor citizens. In Louisiana the poverty rate is 17.4%, which means that these individuals earn less than $13, 590 per year, for a two-person household $18,310 a year and $27,750 for a family of four (https://worldpopulationreview.com/state-rankings/poorest-states).
More than half (65.4%) of Louisiana residents are homeowners and 34.5% rent. Renters in Louisiana appear more cost-burdened than residents in other states. The median gross rent in the state is fairly low when compared to the rest of the US, but the rate of rent stress in Louisiana is the fifth highest in the country. Only Florida, Puerto Rico, California and Hawaii have higher rates of rent stress. Housing in Louisiana is often found lacking adequate kitchen facilities, plumbing and phone service. In 2022, housing conditions are becoming worse due to various economic factors pushing costs beyond household income limits (https://www.lhc.la.gov/2019-louisiana-housing-needs-assessment).
Food Insecurity is defined as the lack of access, at times, to enough food for an active, healthy adult. Food Insecurity is considered a critical public health issue. According to Feeding America Louisiana has 640,540 people (13.7% of the population) currently face hunger in the state (https://map.feedingamerica.org/county/2020/overall/louisiana).
Key Challenges and Advantages
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Caddo, Jefferson, E Baton Rouge and Orleans parishes all have initiatives already in work to encourage healthy lifestyles and improve health and provide more access to health services. | Poorest state for health. |
| LA Dept of Health also has website with health resources, high community support for changes. | Low income households. |
| High poverty. | |
| Areas of high rate of food insecurity. | |
| Areas of high rate of food insecurity. | |
| Increasing unemployment rates. | |
| Not everyone has medical insurance. |
